盧福翊 副教授

盧福翊 副教授
學群:農業及海洋生物科技產業學群
研究專長:魚類發育生物學、魚類生理學
E-mail:fuilu@mail.ncku.edu.tw
研究室:89805
研究室Tel:+886-6-2757575#58218
實驗室Tel:+886-6-2757575#58224#813

| 學校 | 系所 | 國家 | 學位 | 起訖年月 |
| 史特拉斯堡第一大學 | 發育生物學 | 法國 | 博士 |

| 服務機關 | 職稱 | 起訖年月 |
| 國立成功大學 | 副教授 | 2019.08~迄今 |
| 國立成功大學 | 助理教授 | 2014.02~2019.07 |

魚類為了在水中生存,必須調節本身的生理機制來適應在水域環境所遭遇的挑戰(如溫度以及滲透壓的變化等)。所以,我們使用不同的魚種因不同的棲息環境而產生不同的生理特性來做比較。探討水生動物如何調適本身的生理情形來適應外界環境的變化。 除此之外,本實驗室也探討在脊椎動物的早期胚胎發育時期的細胞生理機制,包含了細胞分化以及細胞移動。本實驗室利用斑馬魚作為研究材料,利用其許多特性來方便我們探討在脊椎動物早期發育時期各種基因的功能。對於細胞分化方向包含探討在體軸的不對稱性決定過程。包括前後軸,背腹軸以及左右之不對稱。我們正在探討有哪些訊息傳遞路徑參與在這些體軸決定以及細胞移動的過程以及其控制的機制。
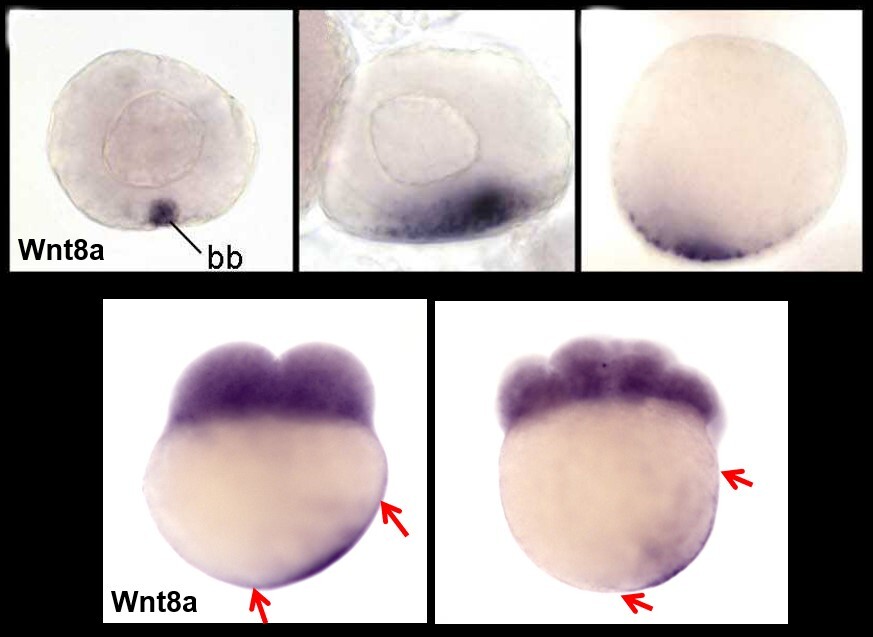 |
The animal-vegetal axis in vertebrates is established during oogenesis, resulting in a radially symmetric egg at ovulation. In anamniotes, fertilization triggers a microtubule-dependent movement of the maternal dorsal determinants, initiating embryonic axis formation. In this study, we identified the vegetal maternal dorsal determinant in fish as Wnt8a mRNA. The migration of Wnt8a mRNA established a dorsal-to-ventral gradient of Wnt signaling that spans the entire embryo. This gradient is limited by two Wnt inhibitors, Sfrp1a and Frzb, which restrict the activation of the beta-catenin pathway to the dorsal marginal blastomeres. Our findings reveal the molecular mechanisms that regulate embryonic axis formation in fish and provide insight into the evolution of axis formation in vertebrates. |
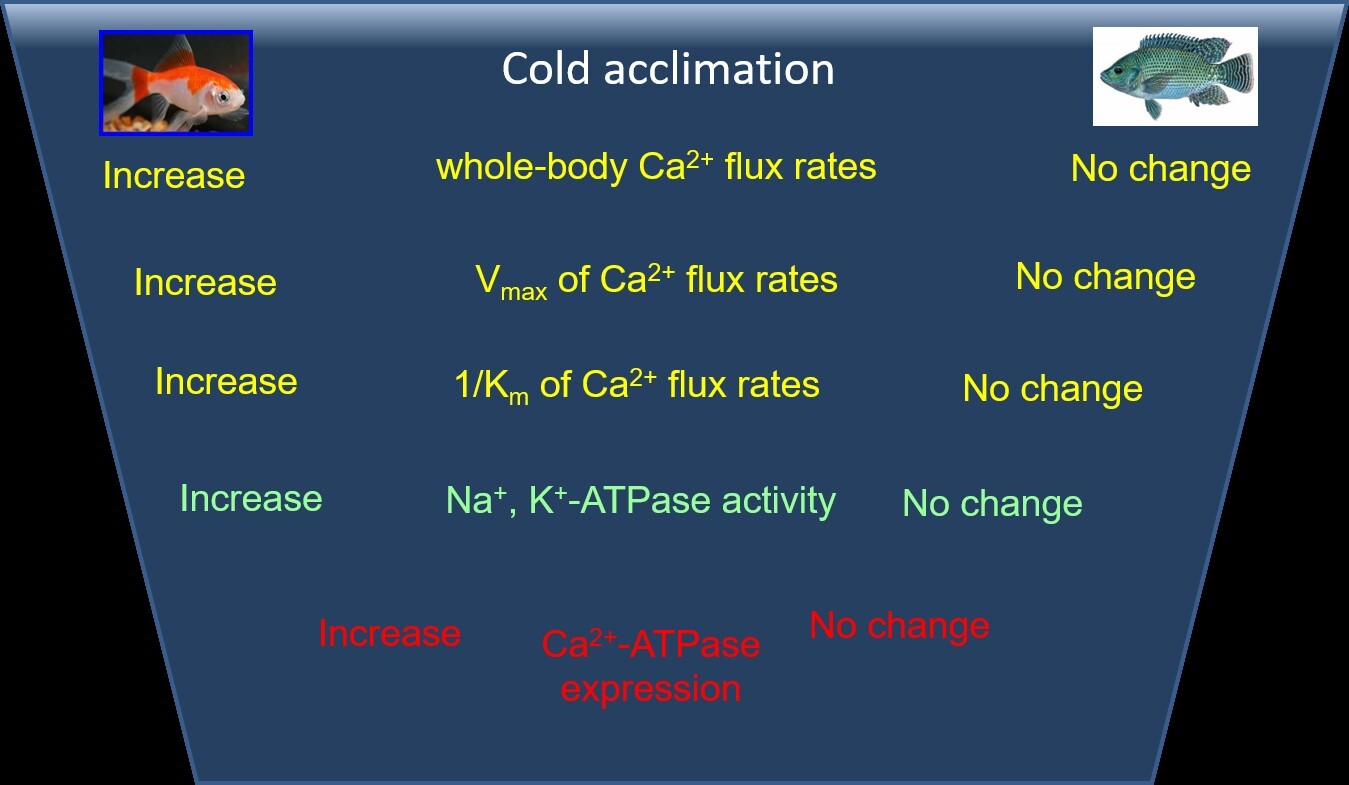 |
Fibrosing Teleost species adjust their body temperature according to the aquatic environment they live in. When water temperature decreases, biochemical reactions and physiological processes, including ion absorption, can be affected. Previous studies have mainly examined the impact of low temperature on plasma ion concentrations or membrane transporters in fishes. In this study, we compared how stenothermic tilapia and eurythermic goldfish acclimate to cold temperatures. Our results showed that long-term cold exposure led to a greater decrease in whole-body calcium content in tilapia than in goldfish. Furthermore, goldfish exhibited better calcium absorption and higher expression of plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase, as well as higher Na+/K+-ATPase activity, which provides the major driving force for ion absorption. These differences may be due to goldfish's more effective regulation of Ca2+ influx kinetics and better maintenance of whole-body calcium content compared to tilapia. |
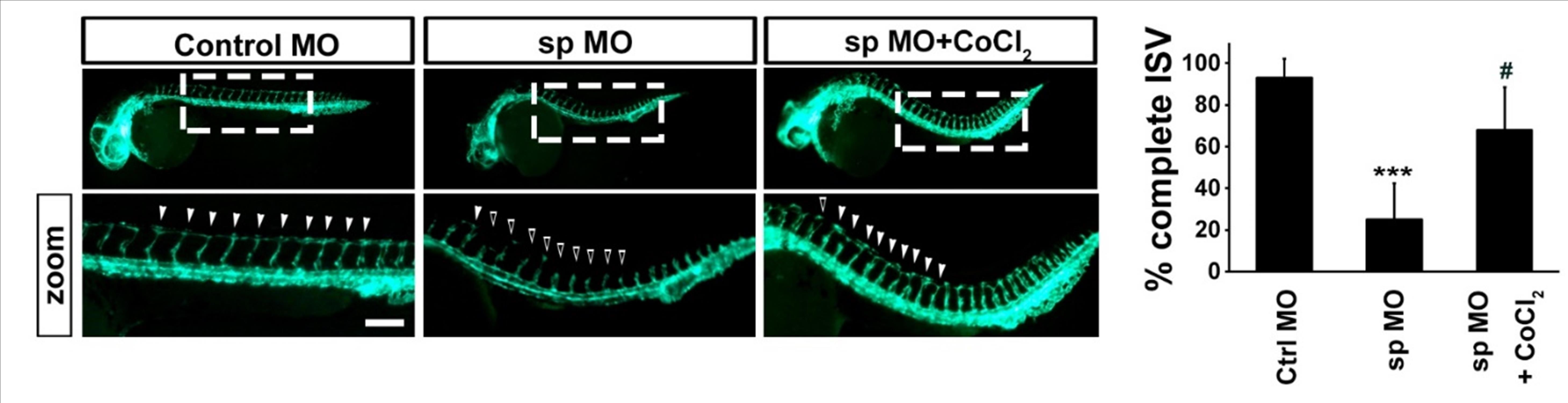 |
EGF is known to promote the formation of new blood vessels by inducing endothelial cell (EC) proliferation and migration. Brefeldin A (BFA)-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange proteins (BIGs) 1 and 2 accelerate the activation of ADP-ribosylation factor (Arf) 1, which regulates vesicular transport between the Golgi and plasma membrane by replacing bound GDP with GTP. While previous studies have suggested that treatment with BFA can inhibit VEGF secretion by interfering with Arf1 activation, the exact role of BIG1 and BIG2 in VEGF trafficking, expression, EC migration and proliferation, and vascular development remains unclear. Our study found that angioblast migration and intersegmental vessel sprouting were impaired when the BIG2 homolog, Arf guanine nucleotide exchange factor (arfgef) 2, was knocked down in zebrafish with the endothelial expression of green fluorescent protein (GFP). Moreover, the depletion of arfgef2 by CRISPR/Cas9 also resulted in vascular development defects in zebrafish embryos. These findings suggest that BIG1 and BIG2 play a crucial role in endothelial cell angiogenesis. (Chen et al., 2020; Han et al., 2018; Li et al., 2022; Lu et al., 2019; Rothschild et al., 2020) |
