洪良宜 教授

洪良宜 教授
學群:生物醫學科技產業學群
研究專長:癌症研究、訊息傳遞、細胞週期基因調控
E-mail:lyhung@mail.ncku.edu.tw
研究室:89903
研究室Tel:+886-6-2757575#58222
實驗室Tel:+886-6-2757575#58234#914

| 學校 | 系所 | 國家 | 學位 | 起訖年月 |
| 國防醫學院 | 生命科學所 | 中華民國 | 博士 | |
| 國立陽明醫學院 | 遺傳研究所 | 中華民國 | 碩士 | |
| 私立中國文化大學 | 生物系 | 中華民國 | 學士 |

| 服務機關 | 職稱 | 起訖年月 |
| 國立成功大學 生物科技中心 | 中心主任 | 2024.12~至今 |
| 國立成功大學 學生事務處 | 學務長 | 2023.02~至今 |
| 國立成功大學 生物科技中心 | 中心副主任 | 2023.02~2024 |
| 國立成功大學 生物科技與產業科學系 | 系主任 | 2022.08~2023.01 |
| 國立成功大學 生物科技與產業科學系 | 教授 | 2016.08~至今 |
| 國立成功大學 | 副教授 | 2012.08~2016.08 |
| 國立成功大學 | 助理教授 | 2009.02~2012.08 |
| 國立成功大學 | 專案助理教授 | 2005.02~2009.01 |
| 中央研究院 | 博士後研究 | 2000.11~2005.01 |

我們實驗室主要研究極光激酶A在癌細胞大量表現的分子調控機制,以及在癌細胞中大量表現CPAP的功能性角色。極光激酶A在許多癌細胞中有不正常的大量表現。透過研究極光激酶A型基因表現的轉錄調控與轉譯調控,我們找到了可以早期診斷以及作為癌症標靶治療的新穎策略。此外,我們也研究極光激酶A在癌細胞中表現對於腫瘤免疫抑制的關聯性。另外,腫瘤微環境會透過促進發炎反應,幫助癌細胞的生長、轉移與惡化。我們發現CPAP蛋白會增加參與發炎反應很重要的兩個轉錄調控因子NF-κB以及STAT3的轉錄活性。我們希望透過研究CPAP蛋白,可以找到新穎有效的治療癌症的策略。
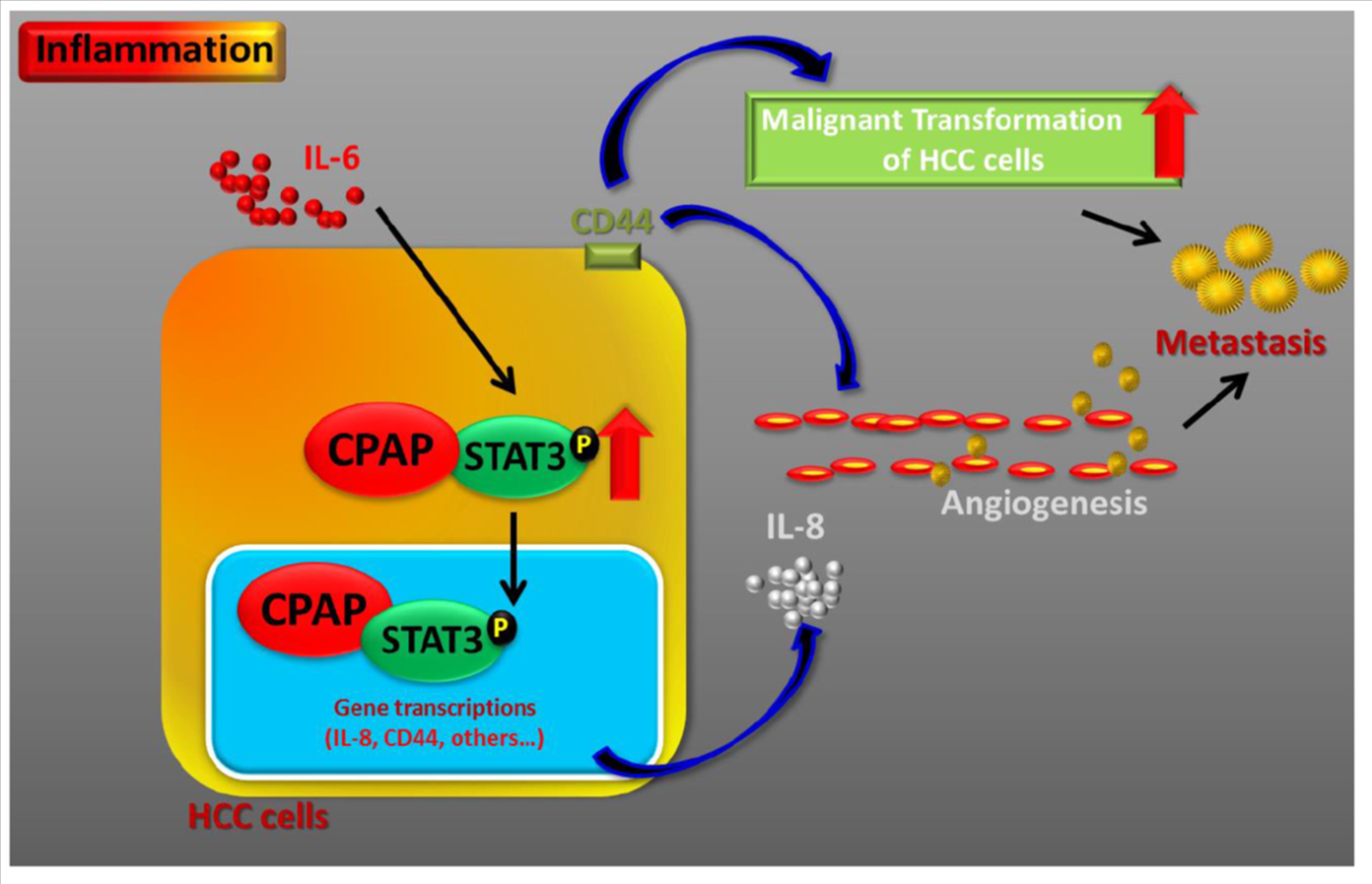 |
Our study demonstrated that CPAP overexpression promotes cancer metastasis and angiogenesis through enhancing IL-6/STAT3 activity, and increases sorafenib, an anti-angiogenesis drug, resistance in HCC. Using ex vivo cell models and in vivo animal models, we demonstrated that CPAP overexpression not only increases cell migration and angiogenesis abilities but also promotes cancer metastasis by enhancing IL-6/STAT3 activity through direct interaction with STAT3. The expression of STAT3 downstream target genes involved in metastasis is increased in CPAP-overexpressing HCC cells. The interacting domain between CPAP and STAT3 was clarified in this study. Blocking the interaction between CPAP and STAT3 diminished the CPAP-enhanced cell migration, angiogenesis, and metastasis in HCC. In conclusion, our study details the important role of CPAP in HCC malignancies and describes a novel interaction between CPAP and STAT3 and their downstream effect in promoting HCC tumor angiogenesis, metastasis, and sorafenib resistance. Results from this study can provide potential therapeutic strategies for treating metastatic HCC. |
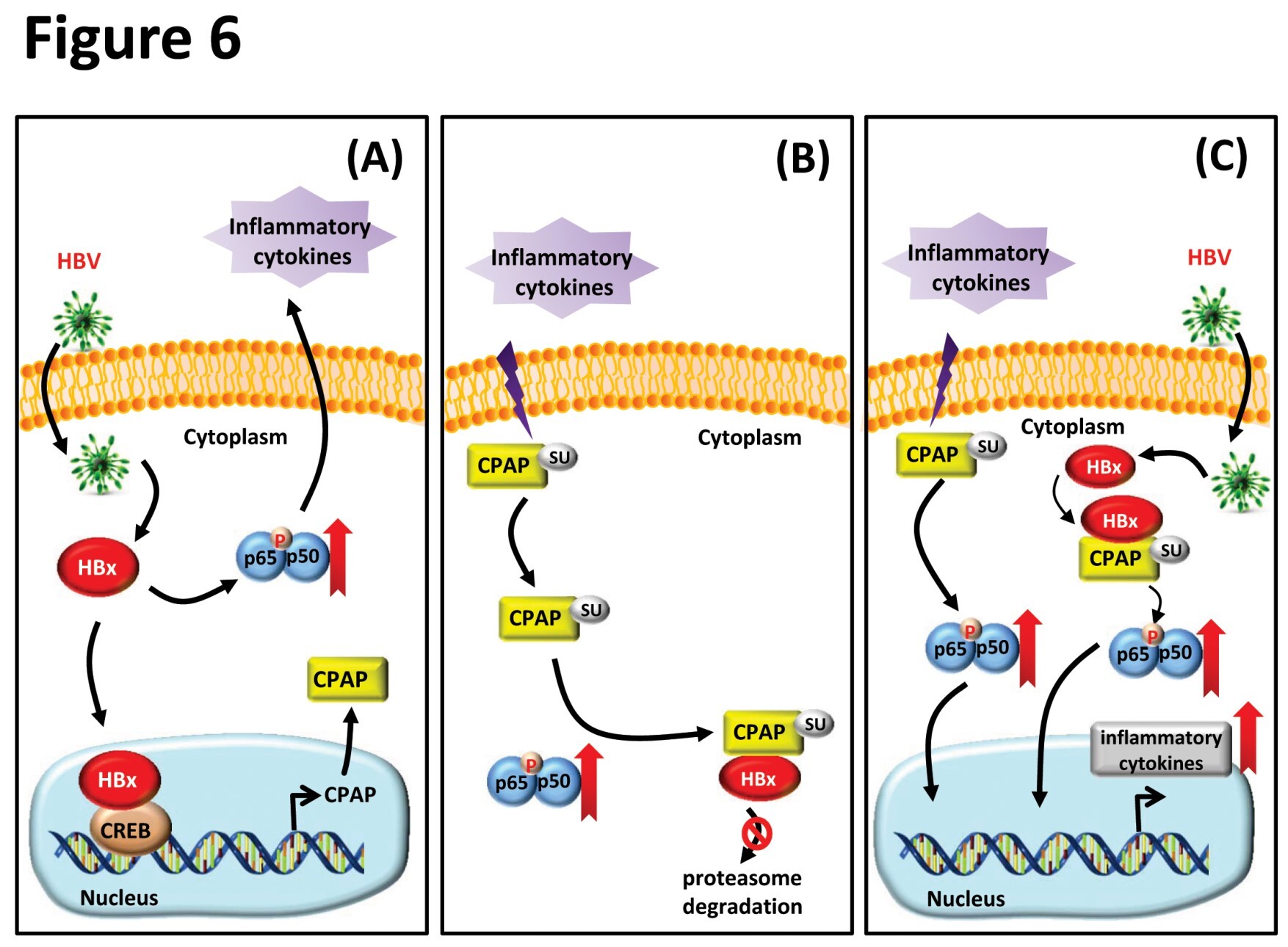 |
Our previous report indicates that TNF-α can induce SUMO-1 modification of CPAP which is required for IKK-mediated NF-κB activation and promotes the growth of HCC cells (Journal of Hepatology 2013, 58(6): 1157-1164). In that report (2013 JH), we presented how CPAP can enhance the transcriptional activity of NF-κB by increasing the phosphorylation of NF-κB/p65 and IκBα through mediating the recruitment of IKKb to the inactivated NF-κB complex. Most interestingly, SUMO-1 modification of CPAP on residues K921 and K975 plays an important role in this pathway. In addition, SUMOylated CPAP collaborates with HBx to increase the NF-κB activity in HBV-associated HCC. In the current study, our results indicated that HBx can transcriptionally up-regulate the expression of CPAP, and overexpressed CPAP can maintain the protein stability of HBx in an NF-κB-dependent manner. The expression level of CPAP and HBx is positively correlated only in the non-tumorous tissues of HCC but not the tumorous tissues. Most importantly, co-expression of HBx and CPAP enhances the abilities of proliferation, migration, and metastasis in both HCC cells and xenograft animal models compared with CPAP- or HBx-expression alone. By transgenic animal model, hepatocyte-specific co-expressed CPAP/HBx double transgenic mouse presents an early incidence of HCC compared with CPAP or HBX single transgenic mouse. Knocked-down expression of CPAP or overexpressed CPAP SUMO-deficiency mutant can block the effects that induced by HBx. |
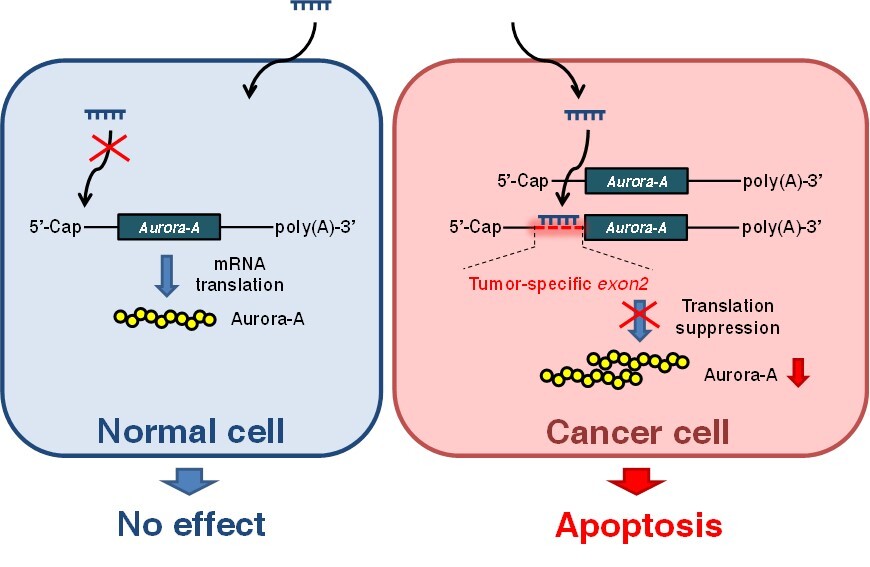 |
Aurora-A inhibitors have been in development for cancer therapy; however, the insufficient specificity and severe side effects of Aurora-A inhibitors raise concern for their use for cancer treatment. Our studies have found that Aurora-A mRNA exon 2, which is located in the 5’-untranslated region (5’-UTR), is predominantly expressed in cancer cells but not the normal cells. This cancer-specific expressed Aurora-A exon 2 makes it a perfect target for developing a novel siRNA-based drug for cancer therapy. This study details a novel Aurora-A exon 2 specific siRNA—siRNA-2—in cancer treatment. Our results demonstrate the specificity, safety, and efficiency of siRNA-2 in anticancer treatment. siRNA-2 effectively and specifically inhibits the translation of exon 2-containing Aurora-A mRNA in cancer cells, but does not affect other Aurora kinases, without affecting normal cells; moreover, locked nucleic acid (LNA) modification of siRNA-2 largely increases its efficacy in inhibiting Aurora-A mRNA translation and anticancer abilities. Both cell models and animal models indicate that LNA-siRNA-2 can decrease cell proliferation and induce apoptosis in cancer cells with no severe side effects. Our results suggest this selective LNA-siRNA-2 has therapeutic potential in Aurora-A-overexpressing cancers. |

| 項目 | 獲獎年 |
| 國立成功大學110學年度教學優良教師 | 2022 |
| 國科會「2022未來科技獎」 | 2022 |
| 指導博士後榮獲111 Grand Review博士生暨博士後研究學術競賽-博士後傑出獎 | 2022 |
| 獲科技部與公益財團法人日本交流協會補助青年人員暑期赴日參訪考察計畫 | 2016 |
| 國立成功大學104學年度優良教師 | 2016 |
| 第十一屆王民寧國內醫藥研究所博士班優秀論文獎 | 2001 |


.svg.png)
