林鼎晏 副教授

林鼎晏 副教授
學群:生物醫學科技產業學群
研究專長:蛋白質交互作用與訊息傳遞
E-mail:lindy@mail.ncku.edu.tw
研究室:89A05
研究室Tel:+886-6-2757575#58229
實驗室Tel:+886-6-2757575#58244#112

| 學校 | 系所 | 國家 | 學位 | 起訖年月 |
| 國防醫學院 | 生命科學所 | 台灣 | 博士 | 1997 ~ 2002 |
| 國防醫學院 | 微生物及免疫所 | 台灣 | 碩士 | 1995~ 1997 |
| 私立高雄醫學院 | 生物學系 | 台灣 | 學士 | 1991~ 1995 |

| 服務機關 | 職稱 | 起訖年月 |
| 國立成功大學 | 副教授 | 2015/02~ 迄今 |
| 國立成功大學 | 助理教授 | 2008/08 ~ 2015/02 |
| 國立成功大學 | 專案計畫助理教授 | 2006/10 ~ 2008/08 |
| 國家衛生研究院 | 博士後研究員 | 2002/10~ 2006/10 |

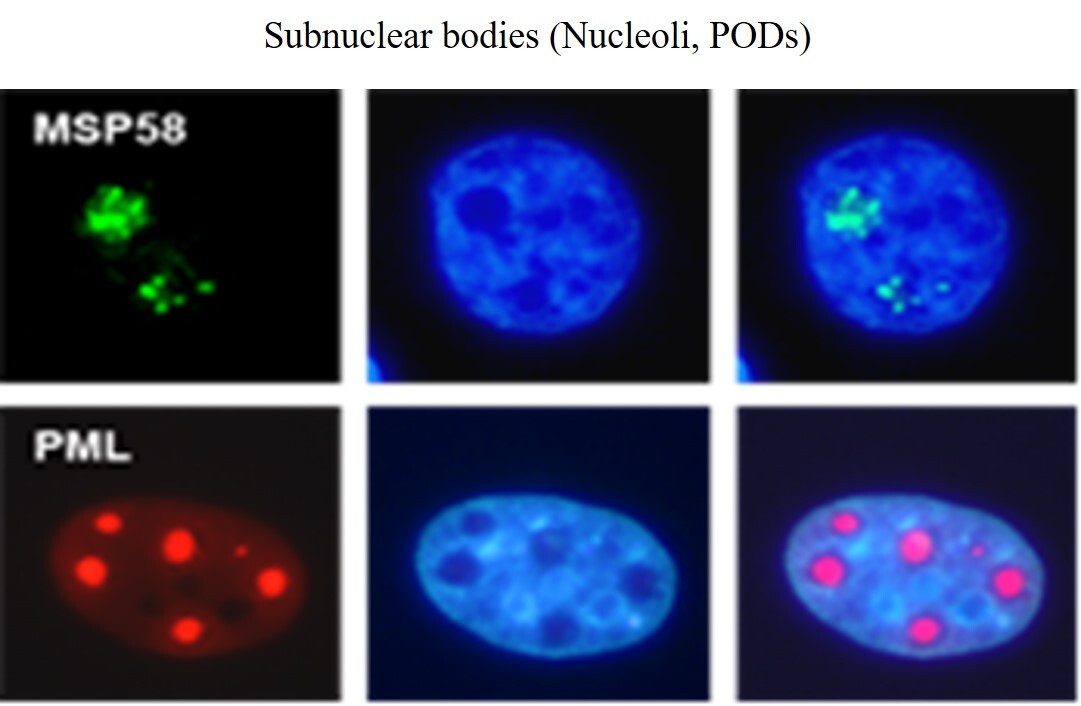
本實驗室主要探討人類核仁蛋白MSP58造成細胞轉型與老化的分子機轉。我們利用酵母菌雙雜交技術找到一些新穎的MSP58結合蛋白,其中包括需ATP的染色質重建複體(chromatin remodeling complex)成員,中心體蛋白與參與端粒酶(telomerase/hTERT)活性的結合蛋白。我們試圖藉由研究MSP58蛋白質在端粒酶與基因轉錄調節功能上了解致癌基因在癌症進展所扮演的角色。另外我們也探討抑癌基因PML與PML核聚體(PODs)調控蛋白質修飾與降解的功能調節與訊息傳遞。目前已發現許多PML/PODs結合蛋白質,並且參與調節蛋白質類泛素化(Sumoylation),活化抑癌基因P53訊息傳遞,DNA修補,細胞凋亡與老化。未來將專注於研究PML與其結合蛋白調節細胞生理功能的分子機轉,以期了解PML抑制癌症進展所扮演的角色。
 |
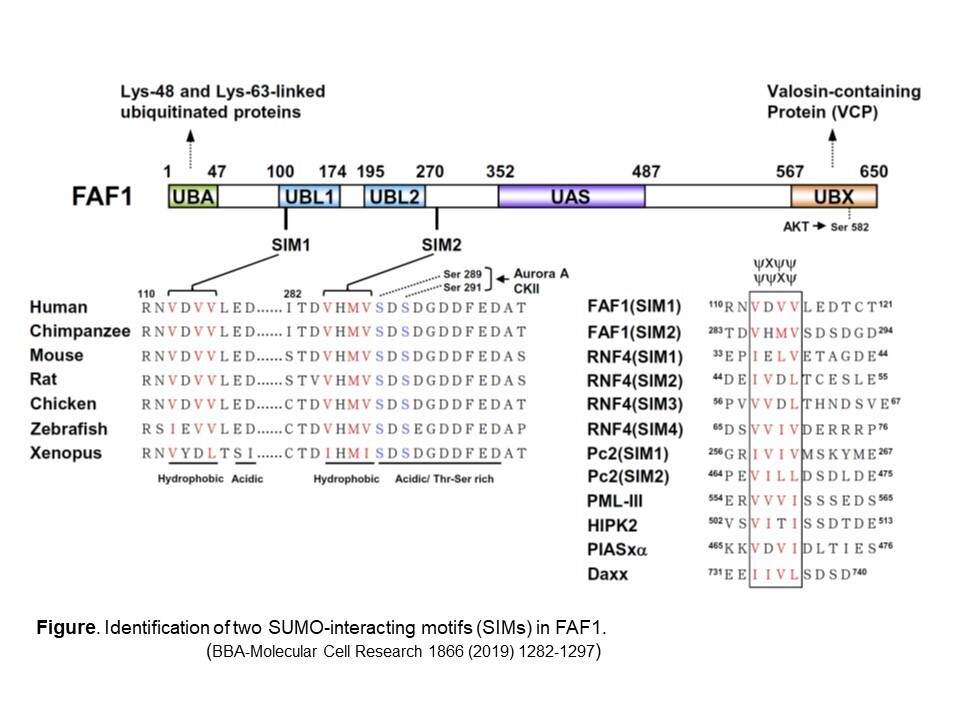
Identification of two SUMO-interacting motifs in Fas-associated factor 1 (FAF1) Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) conjugation (Sumoylation) is known to affect many characteristics of proteins, including their protein-protein interactions, transcriptional regulation functions, subcellular localization and stability. Fas-associated factor 1 (FAF1) is a multidomain protein that interacts with diverse partners to affect numerous cellular processes. Notably, FAF1 participates the proteasomal degradation of ubiquitinated proteins, as it is thought to act as a scaffold protein for multiple ubiquitin-related domains, including ubiquitin-associated (UBA), ubiquitin-like 1 and 2 (UBL1, UBL2), and ubiquitin-regulatory X (UBX) domains. Previously, we discovered two SUMO-interacting motifs (SIMs) within FAF1 that are crucial for binding for sumoylated mineralocorticoid receptor (MR). Additionally, we showed that FAF1 can promote the degradation of MR, thereby inhibiting the its transactivation of target genes. Our work provides novel mechanistic insights into the role of FAF1/SIMs in SUMO-dependent transcriptional modulation and proteolysis. Further work will be required to clarify how the SIMs and ubiquitin-related domains of FAF1 differentially contribute to its regulation of diverse biological processes. |
 |
