黃玲惠 特聘教授

黃玲惠 特聘教授
學群:生物醫學科技產業學群
研究專長:再生醫學科技、生醫材料、組織工程、生化科技、幹細胞生物學
E-mail:lynn@mail.ncku.edu.tw
研究室:89A03
研究室Tel:+886-6-2757575#58227
實驗室Tel:+886-6-2757575#58244#113

| 學校 | 系所 | 國家 | 學位 | 起訖年月 |
| 南加州大學 | 生化及分子生物研究所 | 美國 | 博士 | 1987.09 ~ 1993.05 |
| 國立臺灣大學 | 農化所 | 中華民國 | 碩士 | 1983.09 ~ 1985.06 |
| 國立臺灣大學 | 農業化學系 | 中華民國 | 學士 | 1979.09 ~ 1983.06 |

| 服務機關 | 職稱 | 起訖年月 |
| 國立成功大學國際傷口修復與再生研究中心 | 特聘教授 | 2018-迄今 |
| 國立成功大學生物科技與產業科學系 | 教授/特聘教授 | 2015-迄今 |
| 國立成功大學醫學院臨床醫學研究所 | 教授/特聘教授 | 2006-迄今 |
| 國立成功大學再生醫學卓越研究中心 | 主任 | 2010-2014, 2016-迄今 |
| 國立成功大學生物科技研究所 | 教授 | 1999-2017 |
| 美國史丹福大學醫學院外科學系 | 客座教授 | 2003-2004 |
| 國立成功大學生物科技研究所 | 副教授 | 1998-1999 |
| 國立台灣大學醫學院醫學工程研究中心 | 副研究員兼副教授 | 1994-1998 |

BMT實驗室著眼於推動再生醫學的進展,包括生醫材料,組織工程和細胞治療等領域的研究和產品開發。在過去二十年中,我們獲得了超過92件國際專利,結合了生物化學、細胞生物學、分子生物學、蛋白質體學、化學、材料科學和化學工程等知識和方法,致力於將研究成果轉化為產業應用,以解決臨床醫學問題。BMT實驗室的核心技術包括生產高純度的非重組多孔膠原蛋白基質和濃縮膠原蛋白溶液、有效擴增幹細胞並保持其分化潛力、生物材料的滅菌、膠原蛋白的鑑定和定量、各種傷口敷料的製造、新型生物黏合劑,細胞組織凝膠等以促進組織再生。我們並以嚴謹的動物模式研發世界第一個再生醫學新型藥物,用於有效治療嚴重缺血的肢體使避免截肢。
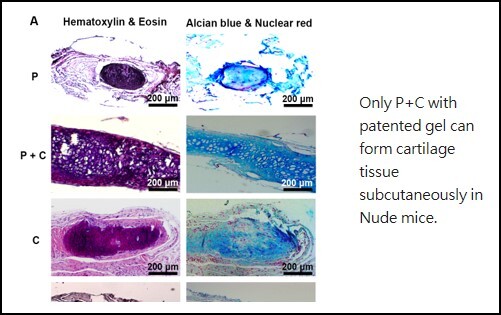 |
De Novo Cartilage Formation Regeneration of cartilage defects has been a key obstacle in clinical practice due to lacking proliferation capacity and dedifferentiation of mature chondrocytes. Since autologous chondrocyte transplantation has been used as a new direction for treating cartilage damage, this study provides a new approach to rejuvenate mature chondrocytes (C cells) to prolong their proliferation capacity and maintain chondrocyte characteristics through influencing by perichondrial progenitor cells (P cells). Our results demonstrate that the passage number of C cells can be prolonged from P6 to P9 and the cell number can be enlarged up to 128 times by co-cultured with P cells. Yet, the cells with chondrocyte characteristics increased cumulatively to 198 times by paracrine effect of P cells. The subcutaneous implantation study significantly demonstrated a synergetic effect of the interaction between P cells and C cells for chondrogenesis and formed an integral cartilage structure. These prominent effects should solve the problem of limited donor sites of cartilage and greatly improve huge needs of chondrocytes clinically. The method can be translated to clinical application directly in which perichondrium can be placed closely to a cartilage defect without extra manipulation of cells, or addition of any growth factors or induction medium. |
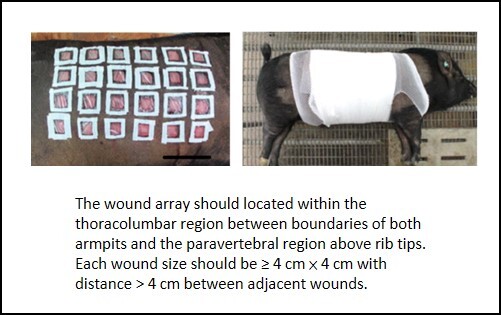 |
Golden Standard of a Wound Array in Pigs There is a tremendous need for an appropriate animal wound model to evaluate the effectiveness of various interventions such as wound dressings, cell therapies, and pharmaceutical agents. For translating research successfully, minipig was chosen owing to its similarity with human beings in aspects of body size, weight, and physiological status. In literatures, wounds of varying sizes were created at varying distances but fail to adequately distinguish the efficacy of various interventions. We attempted to resolve potential drawbacks by developing a systematic wound healing system. No significant variations in dorsal wound closure and contraction were observed within the thoracolumbar region between boundaries of both armpits and the paravertebral region above rib tips. This study has set some golden standards of optimal wound size (≥4 cm × 4 cm) and the minimum distance (˃4 cm) between adjacent wounds to effectively differentiate various interventions. Complied with the 3R principles of animal protocols, this study has established an optimized wound-array model for providing a high-throughput platform not only for precise screening effectiveness of different intervention treatments, but also for examining histological changes and for elucidating underlying molecular mechanisms in the process of wound healing. |
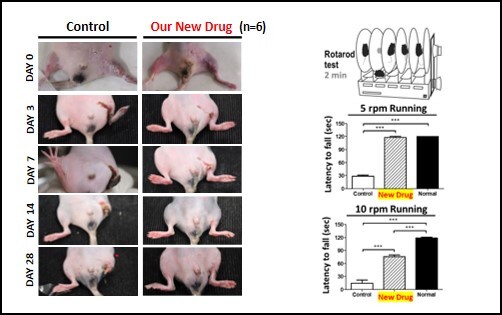 |
Novel Therapy for Critical Limb Ischemia We have developed a first novel pharmaceutical drug using the concept of regenerative medicine to fulfill an unmet clinical need for treating critical limb ischemia (CLI) effectively. Through a harsh assessment platform of a regeneration-deficient murine model with severe ischemic hindlimb, we have proved the success of Grace-001 for ischemic treatments. We have broken through the bottleneck of the existing technologies and have evaluated the efficacy of the drug stringently. Grace-001 can promote neovascularization, neonervation, tissue regeneration and restore blood flow as well as tissue functions. This new drug Grace-001 can effectively retain patients' non-necrotic tissues and prevent CLI limbs from amputation. This new drug not only saves patients' limbs and lives but also rescues economics and heavy burden on national health care. As it comprises of FDA-approved ingredients, its approval can be achieved under the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway and applied to human through a Fast-tract Act. Grace-001 can greatly reduce costs, risk and time to the markets, making it highly advantageous over its competitive therapies such as stem cell therapy and gene therapy. There are more than 8.9 million CLI patients at an annual growth rate of 4.6% in 8 advanced countries with a market more than USD 3.1 billion. |

| 項目 | 獲獎年 |
| 2020未來科技獎 | 2020 |
| 科技部傑出研究獎 | 2017 |
| 教育部生技創新創業獎醫藥生技組銀獎 | 2015 |
| 第十一屆國家新創獎 | 2014 |
| 國際傑出發明家發明終身成就獎。 | 2014 |
| 第十屆國際傑出發明家學術國光獎章 | 2014 |
| 第八屆國際傑出發明家學術國光獎章 | 2012 |
| 國立成功大學延攬及留住特殊優秀人才彈性薪資獎勵 | 2012~2017 |
| 101年度國科會(科技部)獎勵特殊優秀人才 | 2012 |
| 第十五屆俄羅斯阿基米德國際發明展金牌獎 | 2012 |
| 國立成功大學100年度產學合作成果特優教師 | 2012 |
| 100學年度「行政院國家科學委員會補助大專校院獎勵特殊優秀人才」之「研究優良獎」 | 2011 |
| 第五屆波蘭華沙國際發明競賽金牌獎 | 2011 |
| 99學年度「行政院國家科學委員會補助大專校院獎勵特殊優秀人才」之「研究優良獎」 | 2010 |
| 99學年度「李國鼎科技與人文講座」之金質獎章 | 2010 |
| 第七屆國家新創獎 | 2010 |
| 國立成功大學延攬及留住特殊優秀人才獎勵暨科技部獎勵特殊優秀人才 | 2010~2017 |
| 當選Fellow, Biomaterials Science and Engineering (FBSE) | 2008.05 |


.svg.png)
